The ties between us? By the author Aspelin.
Based on social psychological point of view dealing relationship in teaching about the lack of opportunities for operators to meet the "I", which are continuously emerging from a collective experience. Aspelin talking about misguided care, with the help of Sennets theory that the relationship between teacher and student tends to become too intimate, then people will deal with general issues based on personal needs and interests. This principle and the self-obsession that its followers are destroying a skill that people dominated in previous eras, acting art, that is. the ability to play roles. Sennets believe that the desire for intimacy in social relationships, in fact, represents a desire to "subjektivera 'social life. Closeness, warmth, personality and authenticity could discourage socialiteten instead of processing it. How might we see ourselves as close to each other if we are not so distant from each other that we can perceive each other as two unique individuals, as I and you? Sennets theories helps us to highlight the misguided care dilemma. Social care in teaching context is misguided because it aims to satisfy Affekter, in the sense of purely subjective feelings, and not between human emotions. Such psychological focus on supporting and caring for students in danger of breaking down the government met the same building blocks - the social conventions. We can see that the teacher in the previous episode in the book is guided by a imtimitetsideologi, thus creating a sense of closeness and to develop personal relationships in the group, this may seem an implicit objective of his actions. If the teacher's goal is to show concern for the students fail the project thoroughly. The school is not and can not function in therapy, and intimacy needs can be difficult to fill these in teaching. We can not conjure away the expectations laid against us in the respective positions or the institutional situation we are in. Our social interaction is formed based on "interpersonal relationships". What Sennet describe and criticize the alienation process that we are in the book come across as "Uppslukning", which means too little distance in social relations. Sennet points out that there is an inaccurate representation of modern society that IMPERSONALITY and cold is something evil and that intimate relationships are redeeming, I agree. It can be negative in the family, but hardly when it comes to work effectively. According to the author misses Sennet an important aspect of the alienation process that exist in social interactions, thus "överdiffertiering and isolation, therefore, that relationship gets too distant, which is the school's traditional relationship problems.
A productive social life in the teaching situation requires relatively stable interaction rituals, but not what rituationsritualer any time. The symbiotic relationship problem is that which grows the most.
The main threat to the teacher-pupil relationship is that between the realm of teaching players blur. We should not perceive this social psychological theory that either individual or social needs neglected. Both left otillfredställda needs at any one time. The school has been and should have a significant caring role. Let me just supplement my delegation to the above two paragraphs, the school can not deprive a caring responsibilities were, of course, an ideological cause. The school's responsibility in this respect in the governing documents that form the ideological basis for American school. There are moral reasons for the school to pay attention to relational aspects of teaching, because interpersonal relations are moral relationships.
Individual A: behavior toward individual B may always be consequences for their mutual relationship and for individuals separately. The school is not just an abstract phenomenon. It consists of real people, and everyone has a social responsibility.
Relationship in education can therefore be described as either social or individual moments over-emphasized. The operative concept of teacher - pupil - the relationship expressed in this book means that a stable social ties, high degree of harmony and optimal differentiation valued. Based on this reasoning, it is a direct threat to the teacher-pupil ratio is two-fold: first for small and secondly for the great distance between teachers and pupils / students. This implies a direct interaction eye for an eye, as Goffman would put it. What we do claim is to maintain a certain social face. The face is a normative-charged performance that the operator itself is involved in shaping the responses of others, but which nonetheless are crucial. We want to achieve consensus in the relationship. Individuals would like to integrate with one another to belong to the collectivity. This can be achieved only by promoting each other's faces. In this way, the student and teacher dependent on each other, and vice versa, but it is despite the teacher's assessment eye that determines the grade in the relationship, in two senses. Aspelin also discusses I and Me, thus Meads theory. The book has two broad objectives, first to understand the situation in a deep plan and contribute to social psychological theories. During the social interaction space where teachers and students typically aspire to be accepted by each other is an ongoing micro-social process that never can be fully predicted or controlled. Between the teacher and students expressed continuous streams of words and gestures to get his sentence by actors interpretations. The author of kontextuallisera strives concepts, understand their significance in the light of a particular social situation. The empirical studies of methodological approach, which the author quite deliberately chosen. He uses the repetitive nature, therefore he processes a situation and its social event, and again from different angles. Thomas J. Scheffer theory, we can place in the symbolic interaktionismen, he was inspired by Mead, Goffman and Cooley. This theorists is the basis for Aspelin approach, which means "part-overall analysis" and aims to show how the smallest components of the communication process, ie, words and gestures are related to the broader social context in which these characters are part in. Aspelin social psychological orientation may be seen as micro-sociological interaction analysis. The focus is non-verbal communication, therefore feelings. Social Psychology main research field is, in other words, "the problematic relationship between the individual and small socialitet. Scheffer theory is about social ties, which is a relative concept, and refers to a reality between individuals. This concept is abstract and can not therefore be described as a directly observable situation. Ties can be real phenomenon whose existence and nature that can be inferred from the interpretation and analysis of the social context which they are formed. Social ties as normative idea is seen as positive, that is stable and the opposite on the contrary. Social behavior is by stimuli from both inside and outside of a relationship. An overarching goal of relational conscious practice is to build a stable social ties in a school class. Formation of social ties in the teacher-pupil ratio stands or falls on whether a communication is or is not done in an interpersonal sphere, the balance between the individual and social needs. If the communication between teachers and students usually characterized by keeping the beds for stable relationships formed in school class. Social interaction of such nature is in turn a prerequisite for the development of stable social "I". According to Scheffer theory is shame and pride both basic human emotions. Label basic emotions arising from their role is to signal the band's social nature. Shame Feelings indicates that the Social tape threatened or are fragile. Pride Feelings indicates that the relationship is strengthened or is intact. Shame and pride, social emotions in the sense that they brought in a context where the individual sees and evaluates himself by taking other people's perspectives. Put another way occurs shame and pride when the "tune" the self position in relation to the other. Shame seized by negative and pride through positive reconciliation. Stable ties built in the event of a balance between individual and social elements of communication, ie. where the relationship is optimal differential. For great distance leads to isolation and the individual moments over-emphasized. For small distance means similarly to individuals / individual "uppslukas", the social elements over-emphasized. Isolation and uppslukning are indications of two forms of interpersonal alienation. Social ties built through the interaction between the individual and small socialitet. This is done through integration. Aspelin says misguided care aims to ease the pressure, thus allowing internal needs warrants have free rein, he also claims that the interaction regime is perceived as a straitjacket. The school social system that imposes teaching actors strict requirements on what to do and how to do it. The misguided care aimed at the emancipation from this alienation.
Aspelin. J, ties between us, a social psychological perspective on teacher-pupil relationship, (1999). Lost, Stockholm / Stehag
George Herbert Mead sosialpsychology
| We construct our identity through interaction with society. The sentence, consciousness and identity arises not from any source, identity is not in human nature, but they are created in the meeting with the other. The sentence, consciousness and self emerges and develops in the human interaction. Mead explains it through play and games. The child takes first individual roles, such as mother, father, siblings, thus seeing the world with their eyes. The child internalize these roles. By taking mothers, fathers', the police role and generalize it, it creates child them as an abstract mother, an abstract father, an abstract police. This will be the stage for the game. Generalized Ring develops by taking over the role of interaction with the outside world. Then the child can handle different roles at once. They are society's norms and values, as the generalized other. Barnet construct their identity by looking to their internal decentralized roles. Seeing the world with the eyes. You can find its identity and develop it through to internalize the various roles, which then fusing and if we generalize them. Self consists of two main parts: I and Me. In the spontaneous, creative and temporary part of the self. Me are the respective and more stable part of the self. The generalized other is represented by Me. The only living with his professional role as teachers, police, politicians, who only comes from outside society's norms and values have strongly Me at the expense of I. These people represent finished roles. These people can not be creative. They follow the designated roads. If I somehow lost to the self when the man as a robot. Abstract socialization (Simmel Johansson in 1999) leads to Me is moving forward while I will be the weaker. This can cause a weakening of creativity and even cause psychological problems. When I go back and Me is moving forward when life can become meaningless (This can result in burnout (Berg, LE, a compendium of course A). It can also lead to abuse, then you can search liveliness with the help of drugs. In acting on the basis of the perception of the situation and Me immediately after I. I lead to Me changing. Single spontaneous acts may direct response to their surroundings. In the very dynamic and are only temporary, instantaneous. I is the leader and Me is interpretive, constructing. The creative part of the self is I. But I can be creative with the help of Me. Me will create the structure and experience. Experience and the structure is a prerequisite for creativity. In other words generalized other means that the individual in his upbringing takes over the overall values of a given group or a given society covers (Giddens, 2003). Self that awareness developed by individual roles in the form of a playing perspective, which thus completes our consciousness, its meaning and creates the generalized other. Children society into society, they tend to frequent certain to take mother's role and imitate her. It is for the child an individual role. It creates life of his identity and convert it after learning processes for the better and worse. The language is very important for awareness, Self and communication, which will be crucial factor in the understanding of ourselves and others. Gesture may be important, when two people understand what it means and interpret it in the same way, this is a significant symbol. "PASS", will be influenced by significant symbols such as language and interpretations, which may be its content. These two terms creates a signal to other people about the situation. Man is not, but he / she gets to (Johansson, 1999). Just as Simmel stranger and Parks Margin man, so are Meads individuals in many ways indefinite. Memory images reconstructed in the light of the challenges faced by humans present. The past exists only as a social construction in other words. The emphasis on social interaction, self as process, reflexivitet, the constant reorganization of the life histories, subjective ring, lens ring, deeds and so on are today important elements in any social psychological analysis (Johansson, 1999). Literature: Giddens. A. (2003). Sociology. Studentlitteratur Lund Johansson. T. (1999). Social Psychology, Modern theories and perspectives. Studentlitteratur Lund. May. T. (2001). Social Science Research. Studentlitteratur Lund. Mead. G. H. (1995). Self-awareness and society. Grahns PRINTING OFFICE AB: Lund. |
The other sex!- Simon de Beauvoir
Katarina is a single woman living in Gothenburg with their children. She begins at a workshop on Simone de Beauvoir book, the other sex. Where she get girlfriends. Women's objective is to develop itself, through the participation of dental make about their lives with the support of Simone de Beauvoir tanks. Study Circle is not as good as women lose interest, however, they continue to meet. They meet at a cafe called Internationall, and they become very close girlfriends.
Annie becomes Katarinas closest friend. They live near each other. Annie is also a single mother with her daughter, Anna, who is just a half years younger than Stefan. Stefan and Anna share the lives of mothers.
You see the development charity and solidarity between women in the book, which also reflects Troken woman's life, its economic problems and their position as the other sex, which is affiliated to the society.
Katarina loses his best friend Annie. Annie is a charming woman with many lovers but she can not correct relationship with someone. She loves the most, while Katarina Katarina love her most. Kärleket as Katarina Annie will have access shortly after the love of her son and mother. She loves her more than any man, even his brother.
One of the most important in the book is the relationship between mother and child. This one can see the book's front also illustrating a young mother 's community with their children.
Stefan remembers reletionen with his mother. Page 27 pf 2. From the beginning, they were "in the universium alone. A warm dark universium. Soft, quiet, dark and empty. Then it slowly filled by things: the playground, sandbox, buckets, trees, rain, .. Then the people ...
Stefan will go to Paul, to Stockholm. But he does not want to stay there.
Mom, I get well to come back?
Yes, of course, Stefan.
In a week?
Page 264. with Patrik in Jane's apartment. why are you crying?
Stefan is at paul.
For both characterized by Catherine förgråtna face and his own efforts to be an adult and to survive and he had a large hole where the heart would sit.
Stefan, you will become a great man.
As Annie had said for so hundred years ago. A large man with holes in the heart. (250)
Transcendence is the opposite of immanence. (page 42)
The woman was deprived of the opportunity to go out of its present as a passive creature, as the other. Human beings have the capacity to become perfect people through the transcendent scene themselves. But this requires a different consciousness than the patriarchal.
Mike, Stephen's father is especially angry at Annie when she claimed to:
- You should not be so damn sure of himself. How nice is you do not. You fucking (seconds passed, but it was hours, for now were themselves gap, the gap was) whore! (s 81).
- Women said Samuel. There you Stefan, that you must learn right now: They are not to rely on. "(95).
Problems between Mike and Katarina. Page 99.
"There was nothing wrong with him, she thought. He just does not understand: He would not understand. She had not understood what it was like to have children. But the difference was that she had been forced to learn. It had she not been. "(P. 99-100).
Page 105.
Pages 107-108. Children and woman Swedish mode, joint custody.
Stefan feel that being a dad is not the same thing to be home. (112)
Alien to each other. They see one another as the other. "Boyfriend? Said Katarina surprised.
Yes, you know, "said Annie. Such as it hits: Another sex, you know, Katarina: Men and women and so there. "(142)
Stephen's relationship with the father.
Hi papa, I collect stamps. Send as many as you can. Greetings. Stefan. Katarina could see ahead of them how Mike ran around and bought and chose stamps in the United States. As if the stamps could give Stefan the father he would have, but as Stephen himself never shown any interest. ... A postcard father. For the first time she felt compassion for him. .. "Page 173-174.
Mike's letter to his son Stefan: Hi Stefan. How are you? I feel good. I've got a new car, a Ford. Here in the U.S. you have to have a car. There are no sidewalks. I am thinking of you. Dad. "(179).
Problems between Annie and her father.
Is he .. he is ... perverse in any way?
No, no, he is not so perverse, not more than usual in all cases.
To be completely honest, he is disgusting. He is ...
She was looking for org.
-.. a disgust. (187-188)
Why is Catherine not having any? (191).
Samuel testify against Annie. Page 222.
"He makes it to Annie did not want to be with him more." (It is Samuel?) (S 241). He testifies. Page 251.
Katarina (?) Witness (s 253)
Intercourse with Patrik. Her experience. She does not remember exactly (?). you can interpret Frederick? (page 281, pf 2)
Page 295. Katarina laughs Tue, in her own ears her laughter sounds strange, as if she has forgotten how to do when you laugh. "
Humiliation that poor mother. IMPORTANT page. 300
S 310. a bit lesbian. She thinks most about Annie. More than any man.
Page 306. DUALISM?
She did not love her as much as his son Stephen and his mother Sofia. By contrast, she loved her more than her boyfriend, Patrik "fixed in a different way." But she feels unsure what kind of love she hysste to his friend. Why Aniie loved her so much? Därföratt she was loved by her.
Johan Asplund and David Lyon
How does the thunder? This is described in Johan Asplunds book. He describes it by the sound recorder and with words like crash, boom and bang. Asplund discusses scientific thinking on the question "How does the thunder?" He thinks about three different answers:
1 - ashes sounds like thunder. It will be a totologi.
2 - ashes sounds like that! It plays a band and recorded sounds of thunder. It gives nothing of the thunder of those who already know word. It gives the sound as it is. It is objectivity that does not give knowledge.
3 - ashes sounds crash, bang, boom. This option gives something about the thunder. It represents the thunder. Scientific knowledge is largely a representation.
He also shows how to achieve these sound effects in a theater, to illustrate them with the illusion. For me, delusion to fool the senses into thinking that it is reality. To achieve this illusion can roll stones in a trälåda with a prior housing of the plate, then a similar sound of thunder. A simpler alternative to bend a plåtbit with wooden handle and then when sheet metal piece goes back to its original form, the sound of thunder. These solutions have certainly been experiments until its contemporary state of "Drottningholm Theater." Which source device produces the most ASHEN sound? This question is felställd. Both devices produced åskljud in slightly different ways. There is no right or wrong answer (Asplund page 42).
He argues that the social sciences is to understand and to science's job is to explain the problem (Asplund, 2003). In my view, it is both vice-versa. Johan use of the term intelligibilitet and curiosité. These two concepts do not distinguish between explaining and understanding. They are more a concept of curiosity and / or inquisitivness. This makes it a little difficult to understand. An understanding leads us to feel compassion for the person in question and that you then have the opportunity to identify themselves to the other person. This can then lead to the possibility of an intellectual momentum which then becomes an important reason to ask new questions and formulate new answers. This curiosity is an important ingredient to push society forward, there is no curiosity of mankind, so society should stop and not move forward. A small child learns to walk is involved in a process of "instinctive" troubleshooting and as "instinctive" rectification of the resulting errors. This process without so the child would never learn to walk. The same process repeats itself when the child has been a few years older and must learn to cycle. This tested the child's balance. Curious people are doing research and science possible. I would not, of course, argue that a child learns to walk or cycle to be considered as a scientist or researcher. What I want to say is that there is a continuum that extends from child to learn to walk or cycle to the programmer who became Nobel laureates in physics or another and is impossible or unnecessary to point to any particular point in this continuum and say exactly this adopt process engineering or closure of the "scientific" nature.
A concept I settled on in this book was "Simulacrum", I will sort out the concept of significance. Simulacrum must be such that it creates an experience of the striking similarity and at the same time an experience of the discrepancy between illusion and reality. I was yesterday in fifty årsfest, when it was announced that a surprise was on its way after dinner. It came in a man who resembled a priest, should we ask now, I thought. After a moment he took out a bag with rope and a deck of cards, etc.. Then, it was up to me he will conjure for us, I thought no more about it. Suddenly, it was up to me. This is a simulacrum, we see what he does, but still can not understand it. The whole thing is an illusion to the eye, but nonetheless real. His art is to trick our minds to see what he wants us to see and hide their dexterity. It all seems to be an illusion to the eye. Is the answer dexterity that makes it all seems an illusion / art. For me, the answer is YES, whether the painting, magic or mm film. Is a photograph a simulacrum? No, it is not because it tells the truth according to what happens in reality but an illusion. Actually, it is odd to say that a photograph is similar to the avfotograferade motive. The concept of equality requires quietly concept of difference, therefore, duality, according to Lévinas. It is an image and image. Art can be truthful but not, it is an illusion created by this uncertainty to know or not know. It goes without saying that the absence of any discrepancy does nothing new or unexpected has been said. Inventing simulacrum is a very special way to seek knowledge. The products of this knowledge quest are "similarities", similarities involving differences. Simulacrum is like dreaming. Asplund writes the following: the requirement that a simulacrum is not to coincide with what is IMITATE or ILLUSION seems to me far met the "Night Ride". Synesthesia is a person who can make the link visual hearing, but not auditory perception, and vice versa. A synestetisk experience is conscious. Synestetikern have - acute and accidental - experience of a certain color when a certain figure is displayed while a person who has learned to respond with a certain color indication when a certain figure shows have no such experience. Synesthesia is permanent. A synestetiker linking not on one occasion a certain figure with a certain color, and on another occasion the same figure with a different color. The perception is always the same and changed not long time, it is like in old age as it was in childhood. Addicts can get temporary Synesthesia in the use of mescaline and LSD. Humans can also suffer from this condition at the famine at SUNBURN or so. Synestetikern is not mentally ill and can function quite normally in everyday life. Polhem I will not say so much, he was a practitioner who was employed by the king during his time. He was not good at making plans, but he was himself trained, one can say. He was technically smart and dexterous, responsive and so on. On his trips abroad he received additional ideas on various projects such as how to transport materials from the mine mm.
Question 1: Is it possible to manipulate a sense of fully or all of your senses? Is it really, it is not often on the ignorance of the subject. To see things that do not conform with reality.
This book of Lyon describes in a good way developments in a concise format. The book is somewhat confusing Middle otherwise interesting? It captures many well-known sociologists, philosophers, politicians and psychologists.
Post modernity is a concept in today's Western world is described as a globalized world. Post modernity is an idea, cultural, social, and / or perhaps a combination of all three? Lyons writes that he adopts pre, modern and postmodern in a complex interaction. The post is the successor of the modern. It is modern capitalism. It is probably the traditional society in the feudal. Modern society is different from the pre with the pencil's economy, objective relationships between people, big city life, industrialization, individualization, rational thinking. A highly significant number of Western ideas, starting with "Providence", which turned into "progress" and then transferred to the "nihilism". Providence seeks to God's care for the world after its creation, how God oversees historical progress as it moves toward a specific goal. It may be worth serious analytical distinction between post-modernism, with a focus on the cultural, and post modernity, where the social is at the center. The first suggestion that a new kind of society "was taking shape came from Daniel Bell. The new industrial society had taken off in the late 1960s and was based mainly on theoretical knowledge, was formerly the hands especially when working with. The past industrialization would turn into an information society, and this by including new information technologies and communications technologies. The intellectual power would do whatever muscle power had done during the revolution. Bell believes that the post INDUSTRIALISM in fact contributed to the emergence of post modernity. Nihilism is not halted by the delight of services, computers and television, rather, he exploited the possibilities with this. But there were cultural contradictions within capitalism. He stressed that the rationality would be good, and thus could get a new HEDONISM to flourish. The implications of the new technologies will be available in a consumer society. It is inevitable. It must not be forgotten that there will be a higher competition from the rest of Europe. This makes it more costly for the owners and cheaper for consumers. This is, of course, the goal of the goods will even reduce expenditure. Despite this, we should not forget that the disparities are growing in the world, and people who have really much money earn more and yet we have some of the world who can not even write or read. Because they do not have to attend a school. Lyon takes up the positive changes in the form of strike, but is this money hysteria sound? I myself do not believe it, I think Lévinas wrote that some people are constantly hungry because they are never satisfied but are always striving to get more and more, then will it never satisfied during his lifetime. How many have their dream house and the Dream Car, yes it is he who drives around in a cheap car and still feel satisfaction with it. Konsumismen knows no borders. Shopping is no longer a need in some parts of the world, but pure pleasure in some neighborhoods. Bell distinguishes between economics, politics and culture and see science as driving forces for social change, in contrast to the contemporary "culture" narcismens ", discusses Lyotard science itself as a" form of discourse. " Bell sees science as an aspect of the new "axialprincipen", which is more a pure discourse, it is objective, which in Robert Merton classic illustration. Lyotard puts science in connection with the culture and notes that the commercialization of research results that we get an increase in power, but the bargain we miss the truth. There are no guarantees that the reason may release consequences, unfortunately. The social issue is hardly fair, but instead how much injustice there is, and what can we do about it?
Our postmodern condition is completely linked to the consumption of capitalism, our entire society goes back in time, with large classes and a teacher, as a mass. Brand Clothing is our stamp of status, leisure centers will be shut down, and so on. What is it from this? Chaos.
Question 2: What comes after post modernity? Have we any idea or is it a zero world we live in that Asplund would put it.
I think the book was good on the whole, I feel good about what Johan Asplund writes, he writes in an intellectual way. Of disinterest, I think that the last chapter was a little tough to get through, it would have been enough with a description of Christopher Polhem known works, perhaps above all timekeeping movement, and not all of the copper mine mm. This causes kompeplikationer and I love to solve.
How does the thunder? This is described in Johan Asplunds book. He describes it by the sound recorder and with words like crash, boom and bang. Asplund discusses scientific thinking on the question "How does the thunder?" He thinks about three different answers:
1 - ashes sounds like thunder. It will be a totologi.
2 - ashes sounds like that! It plays a band and recorded sounds of thunder. It gives nothing of the thunder of those who already know word. It gives the sound as it is. It is objectivity that does not give knowledge.
3 - ashes sounds crash, bang, boom. This option gives something about the thunder. It represents the thunder. Scientific knowledge is largely a representation.
He also shows how to achieve these sound effects in a theater, to illustrate them with the illusion. For me, delusion to fool the senses into thinking that it is reality. To achieve this illusion can roll stones in a trälåda with a prior housing of the plate, then a similar sound of thunder. A simpler alternative to bend a plåtbit with wooden handle and then when sheet metal piece goes back to its original form, the sound of thunder. These solutions have certainly been experiments until its contemporary state of "Drottningholm Theater." Which source device produces the most ASHEN sound? This question is felställd. Both devices produced åskljud in slightly different ways. There is no right or wrong answer (Asplund page 42).
He argues that the social sciences is to understand and to science's job is to explain the problem (Asplund, 2003). In my view, it is both vice-versa. Johan use of the term intelligibilitet and curiosité. These two concepts do not distinguish between explaining and understanding. They are more a concept of curiosity and / or inquisitivness. This makes it a little difficult to understand. An understanding leads us to feel compassion for the person in question and that you then have the opportunity to identify themselves to the other person. This can then lead to the possibility of an intellectual momentum which then becomes an important reason to ask new questions and formulate new answers. This curiosity is an important ingredient to push society forward, there is no curiosity of mankind, so society should stop and not move forward. A small child learns to walk is involved in a process of "instinctive" troubleshooting and as "instinctive" rectification of the resulting errors. This process without so the child would never learn to walk. The same process repeats itself when the child has been a few years older and must learn to cycle. This tested the child's balance. Curious people are doing research and science possible. I would not, of course, argue that a child learns to walk or cycle to be considered as a scientist or researcher. What I want to say is that there is a continuum that extends from child to learn to walk or cycle to the programmer who became Nobel laureates in physics or another and is impossible or unnecessary to point to any particular point in this continuum and say exactly this adopt process engineering or closure of the "scientific" nature.
A concept I settled on in this book was "Simulacrum", I will sort out the concept of significance. Simulacrum must be such that it creates an experience of the striking similarity and at the same time an experience of the discrepancy between illusion and reality. I was yesterday in fifty årsfest, when it was announced that a surprise was on its way after dinner. It came in a man who resembled a priest, should we ask now, I thought. After a moment he took out a bag with rope and a deck of cards, etc.. Then, it was up to me he will conjure for us, I thought no more about it. Suddenly, it was up to me. This is a simulacrum, we see what he does, but still can not understand it. The whole thing is an illusion to the eye, but nonetheless real. His art is to trick our minds to see what he wants us to see and hide their dexterity. It all seems to be an illusion to the eye. Is the answer dexterity that makes it all seems an illusion / art. For me, the answer is YES, whether the painting, magic or mm film. Is a photograph a simulacrum? No, it is not because it tells the truth according to what happens in reality but an illusion. Actually, it is odd to say that a photograph is similar to the avfotograferade motive. The concept of equality requires quietly concept of difference, therefore, duality, according to Lévinas. It is an image and image. Art can be truthful but not, it is an illusion created by this uncertainty to know or not know. It goes without saying that the absence of any discrepancy does nothing new or unexpected has been said. Inventing simulacrum is a very special way to seek knowledge. The products of this knowledge quest are "similarities", similarities involving differences. Simulacrum is like dreaming. Asplund writes the following: the requirement that a simulacrum is not to coincide with what is IMITATE or ILLUSION seems to me far met the "Night Ride". Synesthesia is a person who can make the link visual hearing, but not auditory perception, and vice versa. A synestetisk experience is conscious. Synestetikern have - acute and accidental - experience of a certain color when a certain figure is displayed while a person who has learned to respond with a certain color indication when a certain figure shows have no such experience. Synesthesia is permanent. A synestetiker linking not on one occasion a certain figure with a certain color, and on another occasion the same figure with a different color. The perception is always the same and changed not long time, it is like in old age as it was in childhood. Addicts can get temporary Synesthesia in the use of mescaline and LSD. Humans can also suffer from this condition at the famine at SUNBURN or so. Synestetikern is not mentally ill and can function quite normally in everyday life. Polhem I will not say so much, he was a practitioner who was employed by the king during his time. He was not good at making plans, but he was himself trained, one can say. He was technically smart and dexterous, responsive and so on. On his trips abroad he received additional ideas on various projects such as how to transport materials from the mine mm.
Question 1: Is it possible to manipulate a sense of fully or all of your senses? Is it really, it is not often on the ignorance of the subject. To see things that do not conform with reality.
This book of Lyon describes in a good way developments in a concise format. The book is somewhat confusing Middle otherwise interesting? It captures many well-known sociologists, philosophers, politicians and psychologists.
Post modernity is a concept in today's Western world is described as a globalized world. Post modernity is an idea, cultural, social, and / or perhaps a combination of all three? Lyons writes that he adopts pre, modern and postmodern in a complex interaction. The post is the successor of the modern. It is modern capitalism. It is probably the traditional society in the feudal. Modern society is different from the pre with the pencil's economy, objective relationships between people, big city life, industrialization, individualization, rational thinking. A highly significant number of Western ideas, starting with "Providence", which turned into "progress" and then transferred to the "nihilism". Providence seeks to God's care for the world after its creation, how God oversees historical progress as it moves toward a specific goal. It may be worth serious analytical distinction between post-modernism, with a focus on the cultural, and post modernity, where the social is at the center. The first suggestion that a new kind of society "was taking shape came from Daniel Bell. The new industrial society had taken off in the late 1960s and was based mainly on theoretical knowledge, was formerly the hands especially when working with. The past industrialization would turn into an information society, and this by including new information technologies and communications technologies. The intellectual power would do whatever muscle power had done during the revolution. Bell believes that the post INDUSTRIALISM in fact contributed to the emergence of post modernity. Nihilism is not halted by the delight of services, computers and television, rather, he exploited the possibilities with this. But there were cultural contradictions within capitalism. He stressed that the rationality would be good, and thus could get a new HEDONISM to flourish. The implications of the new technologies will be available in a consumer society. It is inevitable. It must not be forgotten that there will be a higher competition from the rest of Europe. This makes it more costly for the owners and cheaper for consumers. This is, of course, the goal of the goods will even reduce expenditure. Despite this, we should not forget that the disparities are growing in the world, and people who have really much money earn more and yet we have some of the world who can not even write or read. Because they do not have to attend a school. Lyon takes up the positive changes in the form of strike, but is this money hysteria sound? I myself do not believe it, I think Lévinas wrote that some people are constantly hungry because they are never satisfied but are always striving to get more and more, then will it never satisfied during his lifetime. How many have their dream house and the Dream Car, yes it is he who drives around in a cheap car and still feel satisfaction with it. Konsumismen knows no borders. Shopping is no longer a need in some parts of the world, but pure pleasure in some neighborhoods. Bell distinguishes between economics, politics and culture and see science as driving forces for social change, in contrast to the contemporary "culture" narcismens ", discusses Lyotard science itself as a" form of discourse. " Bell sees science as an aspect of the new "axialprincipen", which is more a pure discourse, it is objective, which in Robert Merton classic illustration. Lyotard puts science in connection with the culture and notes that the commercialization of research results that we get an increase in power, but the bargain we miss the truth. There are no guarantees that the reason may release consequences, unfortunately. The social issue is hardly fair, but instead how much injustice there is, and what can we do about it?
Our postmodern condition is completely linked to the consumption of capitalism, our entire society goes back in time, with large classes and a teacher, as a mass. Brand Clothing is our stamp of status, leisure centers will be shut down, and so on. What is it from this? Chaos.
Question 2: What comes after post modernity? Have we any idea or is it a zero world we live in that Asplund would put it.
Traditional schools
There are three major traditions in sociological social psychology: symbolic interactionism, social cognition, and social exchange theory.[6] Although they are not mutually exclusive, these traditions have tended to provide the main theoretical orientations by which scientists have treated social research.
Symbolic interactionism
- Main article: Symbolic interactionism
Symbolic interactionism (or SI) is a sociological tradition originating out of the ideas of George Herbert Mead and Max Weber. The symbolic interactionists emphasize that human life is governed by meaningful interactions between persons. There are two major schools of SI: Structural SI and Process SI. Structural SI uses shared social knowledge from a macro-level (i.e., at the level of the organization and institution) to explain relatively static patterns of social interaction and psychology at the micro-level. Structural SI researchers tend to use quantitative methods. Identity Theory[7] and Affect Control Theory[8] grew out of this tradition. By contrast, Process SI stems from the Second Chicago School and views social interactions to be constant flux, studying it without reference to a larger social structure. Process SI researchers tend to use qualitative and ethnographic methods.
Social exchange
- Main article: Social exchange theory
Social exchange theory emphasizes the idea that social action is the result of personal choices made by considering relative benefits and costs. The theory of social exchange predicts that people will make choices with the intention of maximizing benefits. A key component of this theory is the postulation of the "comparison level of alternatives", which is the actor's sense of the best possible alternative (i.e., the choice with the highest benefits relative to costs).[3]
In this sense, theories of social exchange share many essential features with classical economic theories like rational choice theory. However, social exchange theories differ from economic theories by making predictions about the relationships between persons, and not just the evaluation of goods. For example, social exchange theories have been used to predict human behavior in romantic relationships by taking into account each actor's subjective sense of costs (i.e., volatility, economic dependence), benefits (i.e., attraction, chemistry, attachment), and comparison level of alternatives (i.e., if any viable alternative mates are available).[3]
General information on the social psychology emergence
| Social Psychology came to the first in the early 1900s. The largest that I know and the best known of them is Charles Horton Cooley with the book "Human nature and the social order. So that you can see the social order itself, as a part of society (Being a mirror himself). I think Charles is interpreted in a way, or it's my own interpretation of the Charles. The first textbooks were first six years later by EA Ross and William McDougall. The first author approached the social psychology from a sociological outlook and the latter from a psychological perspective. It came a couple of newspapers, which concerned the substance but they were quite muddled and I choose not to take them up on my page (Journal of Personality and Social Psychology). |
SP History
McDougall himself did not have a grand vision for social psychology, and by default regarded it as a subfield of psychology (albeit an eminently useful one).[5] For a period during the early- to mid-twentieth century, social psychology was conceived as an interdisciplinary effort, capable of addressing those issues which psychologists and sociologists had in common. However, the tide turned sharply against these interdisciplinarians, as many of those research bodies which had attempted to find common intellectual ground broke down under the strain of various academic pressures. As a result, social psychology was bifurcated into two traditions: those allied with psychology who sought to explain how the minds of individuals are influenced by social factors, and those allied with sociology who understood human action as being embedded in (and determined largely by) a rich network of human relationships.
Today, for better or worse, the sociological and psychological traditions of social psychology maintain relatively little contact with one another. Sociological social psychologists tend to publish in Social Psychology Quarterly (formerly Sociometry), while psychological social psychologists publish elsewhere. Also, sociological social psychologists usually are members of the social psychology section of the American Sociological Association (ASA), while psychological social psychologists belong to other organizations.
A fair body of fruitful research exists in sociological social psychology. The great emphasis many American psychological social psychologists have placed on intraindividual processes has distinguished them from many non-U.S. social psychologists. In many areas, sociological social psychologists have demonstrated greater collaboration and complementary theoretical interests with psychological social psychologists in other English speaking countries.
In subject matter, sociological social psychology continues to draw upon neighboring social sciences like psychological social psychology and micro-economics, as well as upon social philosophy, while maintaining its own approaches to investigation.
The discipline of social psychology began at the start of the twentieth century. A list of landmark moments would have to include the publication of Charles Horton Cooley's "Human Nature and Social Order" in 1902. Cooley's effort sought to explain the social order by use of the concept of a looking glass self, and to explain the notion of the self as essentially the same as the notion of "society".[3]
The first textbooks in social psychology would be published six years later by E. A. Ross and William McDougall.[4] The former approached the topic from a sociological standpoint, and the latter from a psychological one. The first major journal in social psychology would be the Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology in 1922 (later Journal of Personality and Social Psychology).[3]
McDougall himself did not have a grand vision for social psychology, and by default regarded it as a subfield of psychology (albeit an eminently useful one).[5] For a period during the early- to mid-twentieth century, social psychology was conceived as an interdisciplinary effort, capable of addressing those issues which psychologists and sociologists had in common. However, the tide turned sharply against these interdisciplinarians, as many of those research bodies which had attempted to find common intellectual ground broke down under the strain of various academic pressures. As a result, social psychology was bifurcated into two traditions: those allied with psychology who sought to explain how the minds of individuals are influenced by social factors, and those allied with sociology who understood human action as being embedded in (and determined largely by) a rich network of human relationships.
Today, for better or worse, the sociological and psychological traditions of social psychology maintain relatively little contact with one another. Sociological social psychologists tend to publish in Social Psychology Quarterly (formerly Sociometry), while psychological social psychologists publish elsewhere. Also, sociological social psychologists usually are members of the social psychology section of the American Sociological Association (ASA), while psychological social psychologists belong to other organizations.
A fair body of fruitful research exists in sociological social psychology. The great emphasis many American psychological social psychologists have placed on intraindividual processes has distinguished them from many non-U.S. social psychologists. In many areas, sociological social psychologists have demonstrated greater collaboration and complementary theoretical interests with psychological social psychologists in other English speaking countries.
In subject matter, sociological social psychology continues to draw upon neighboring social sciences like psychological social psychology and micro-economics, as well as upon social philosophy, while maintaining its own approaches to investigation.
Social Psychological expriment?
Well known experiments and studies that have influenced social psychology include:
- The Asch conformity experiments from the 1950s, a series of studies that starkly demonstrated the power of conformity on people's estimation of the length of lines (Asch, 1955). On over a third of the trials, participants conformed to the majority, even though the majority judgment was clearly wrong. Seventy-five percent of the participants conformed at least once during the experiment.
- Muzafer Sherif's (1954) Robbers' Cave Experiment, which divided boys into two competing groups to explore how much hostility and aggression would emerge. Also known as realistic group conflict theory, because the intergroup conflict was induced through competition over resources.
- Leon Festinger's cognitive dissonance experiment, in which subjects were asked to perform a boring task. They were divided into 2 groups and given two different pay scales. At the end of the study, some participants were paid $1 to say that they enjoyed the task and another group of participants was paid $20 to say the same lie. The first group ($1) later reported liking the task better than the second group ($20). People justified the lie by changing their previously unfavorable attitudes about the task (Festinger & Carlsmith, 1959).
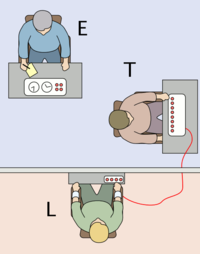
- The Milgram experiment, which studied how far people would go to obey an authority figure. Following the events of The Holocaust in World War II, the experiment showed that normal American citizens were capable of following orders to the point of causing extreme suffering in an innocent human being (Milgram, 1975).
- Albert Bandura's Bobo doll experiment, which demonstrated how aggression is learned by imitation (Bandura, et al., 1961). This was one of the first studies in a long line of research showing how exposure to media violence leads to aggressive behavior in the observers.
- The Stanford prison experiment, by Philip Zimbardo, where a simulated exercise between student prisoners and guards showed how far people would follow an adopted role. This was an important demonstration of the power of the immediate social situation, and its capacity to overwhelm normal personality traits (Haney, Banks, & Zimbardo, 1973).



